Spark Plug Function Under Small Load
PROJECTION OF THE SPARK PLUG INSULATOR NOSE INTO THE COMBUSTION CHAMBER
By projecting the insulator nose into the combustion chamber the insulator nose cooling increases by flow of the cold air of the mixture sucked in at high revolutions of the engine and conversely the nose is heated fast at small revolutions.

SPARK PLUG ELECTRODE WITH HIGH THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY
The center electrode with high thermal conductivity is made of a composite material of the nickel alloy and copper core or of the nickel alloy with yttrium. Big thermal conductivity of the electrode enables use of a bigger area of the insulator nose for the same self-ignition temperature of the spark plug. The advantage is also a period necessary for depositing the insulator nose and better functioning of the spark plug under small load.

CYLINDRICAL ENDING OF THE SPARK PLUG INSULATOR NOSE
Cylindrical ending of the insulator nose accelerates obtaining of the insulator nose operating temperature already within the first seconds of the engine running.

REDUCED SPARK PLUG CENTER ELECTRODE AND PROJECTION OF THE SPARK PLUG SHELL INTO THE COMBUSTION CHAMBER
Combination of the insulator nose cylindrical shape together with reduction of the center electrode end diameter and projection of the shell into the combustion chamber is the optimal design ensuring a perfect function of the spark plug under low engine load but also at full performance.

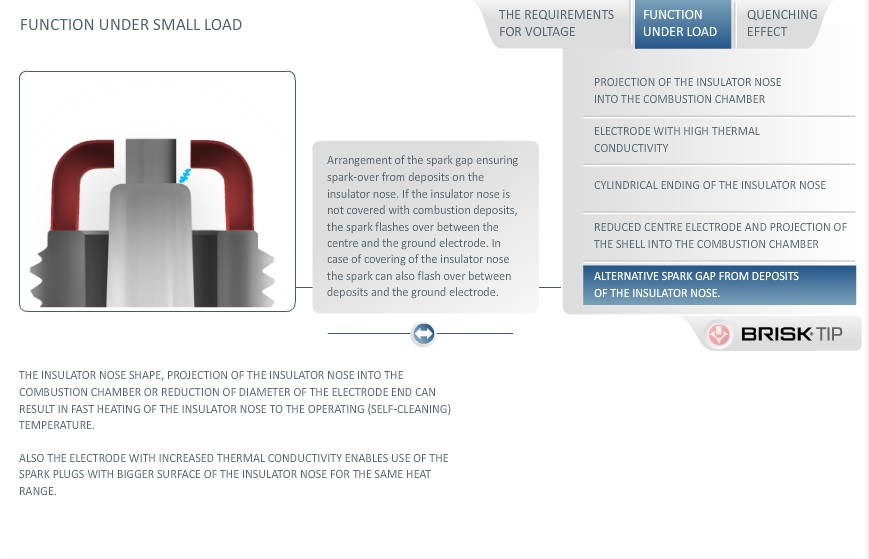
ALTERNATIVE SPARK GAP FROM DEPOSITS ON THE SPARK PLUG INSULATOR NOSE
Arrangement of the spark gap ensuring spark-over from deposits on the insulator nose. If the insulator nose is not covered with combustion deposits, the spark flashes over between the center and the ground electrode. In case of covering of the insulator nose the spark can also flash over between deposits and the ground electrode.